No. 533 AUGUST 2015 Edited by Stephen Brunning
HADAS DIARY 2015/16
Tuesday 15th to Saturday 19th September: Trip to the New Forest.
Tuesday 13th October @ 8pm: Scientific Methods in Archaeology. Lecture by Dr Caroline Cartwright.
Tuesday 12th November @ 8pm: The history of the Royal National Lifeboat Institution. Lecture by Keith Cunningham.
Sunday 6th December: Christmas Party at Avenue House. Further details coming soon.
Tuesday 10th January @8pm: Royal Palaces of Enfield. Lecture by Ian Jones (EAS).
Tuesday 9th February @8pm: Medieval Middlesex: The Archaeological Remains. Lecture by Adam Corsini.
Tuesday 8th March @8pm: Crossrail Archaeology Project. Lecture by Jay Carver.
All Lectures are held at Stephens House & Gardens (Avenue House), 17 East End Road, Finchley, N3 3QE, and start promptly at 8.00 pm, with coffee /tea and biscuits afterwards. Non-members welcome (£1.00). Buses 82, 125, 143, 326 & 460 pass nearby and Finchley Central Station (Northern line) is a short walk away.
—————————————————————————————————————-
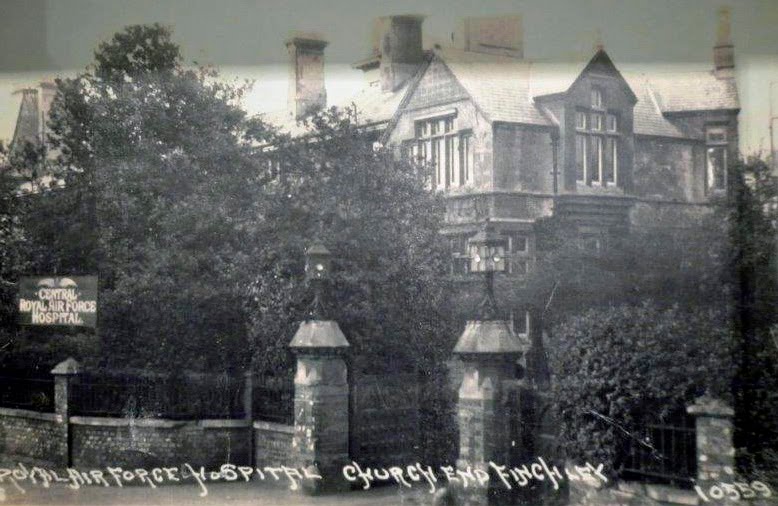
Update on RAF Central Hospital. By Don Cooper.
Following the short article on Stephens House and Gardens (formerly Avenue House) as a Royal Air Force (RAF) hospital in last month’s newsletter (July no 532), Peter Elliott, Head of Archives at the RAF Museum, Hendon sent the following email:
“The piece on the RAF Hospital mentions Son Ld. H E Whittingham. He became Air Marshal Sir Harold Whittingham, Director of RAF Medical Services, and his papers are held by the Wellcome Library under their reference PP/HEW”.
Archaeological Priority Areas. By Peter Pickering.
The Greater London Archaeological Advisory Service (GLAAS) is now part of Historic England – the organisation created to look after the remainder of English Heritage’s activities after the owning and running of ancient monuments had been hived off. It maintains London’s Historic Environment Record and provides archaeological advice to all the boroughs except Southwark and the City. GLAAS has started a programme to review, revise and update the Archaeological Priority Areas across Greater London.
Archaeological Priority Areas are areas where there is significant known archaeological interest or particular potential for new discoveries. A planning application for development in an Archaeological Priority Area may trigger an archaeological condition, requiring anything from a watching brief to a full scale excavation. (Our lecture in April about Mill Hill Barracks demonstrated what new knowledge an archaeological condition can bring forth.) Barnet’s Local Plan includes a map of thirty-four such areas. HADAS was involved when the Local Plan was being revised in 2011 and 2012.
GLAAS keeps an eye on all planning applications received by Barnet Council, and asks the Council to impose an archaeological condition when it thinks that is appropriate. HADAS also tries to monitor applications that come to our attention, and make our own representations to GLAAS and to the Council.
Of course, it is only a small minority of the many planning applications received by the Council, even in Archaeological Priority Areas, where an archaeological condition may be warranted – most planning applications involve little or no disturbance of the ground, and will not therefore affect any buried remains. An application affecting a historic building or conservation area may require special consideration, but Listed Building and Conservation Area Consents are different from archaeological conditions, and do not involve GLAAS. According to GLAAS, London’s Archaeological Priority Areas need to be modernised; they were created piecemeal over 25 years ago, and there are inconsistencies. Many boroughs’ areas lack a supporting evidence base; do not always reflect current archaeological knowledge or today’s priorities (HADAS believes that Barnet’s is one of the better and more up-to-date plans). GLAAS wish to provide a consistent framework for documenting archaeological interest for planning purposes; a sound evidence base and practical tool for strategic planning. Somewhat controversially they propose to introduce four tiers, three covering the existing Archaeological Priority Areas and one the rest of London; Tier 1 would be specific heritage assets of national significance; Tier 2 local areas where there is specific evidence of the presence or likely presence of heritage assets of archaeological interest; Tier 3 local areas where there is evidence of a potential for heritage assets of archaeological interest.
GLAAS’s ideas are logical and well thought through (though the little notice it takes of local archaeological societies and the work we all do is disappointing). I am somewhat concerned, however, that a system of tiers will cause confusion, and the comprehensive revision of local plans that they will require will impose too much of a burden on GLAAS itself, and on the boroughs, and will therefore take a long time, leaving an unsatisfactory transition period. I also wonder at the impact of the Government’s very recent proposals for substantial deregulation of development in the interests of building more houses, quickly.
An appeal to budding authors. By Jim Nelhams.
Do you visit museums or other places of historical interest, local or otherwise? If so, why not share information with other HADAS members by providing a short note about them.
Our editors work hard to produce your monthly newsletter, but they do not write the information, and very often, they have nothing to publish until shortly before we go to press. Some articles, such as lecture reports, need timely publication. Articles about museums and places of interest do not need to be published immediately. We would like to build up a “library” of write-ups, from which any editor can locate more material. This would help our editors and make their task less stressful.
So if you visit somewhere interesting, why not write a note and send it to me. (see p.12) And remember that by telling us about these places, you are also helping the museums by encouraging members to visit them.
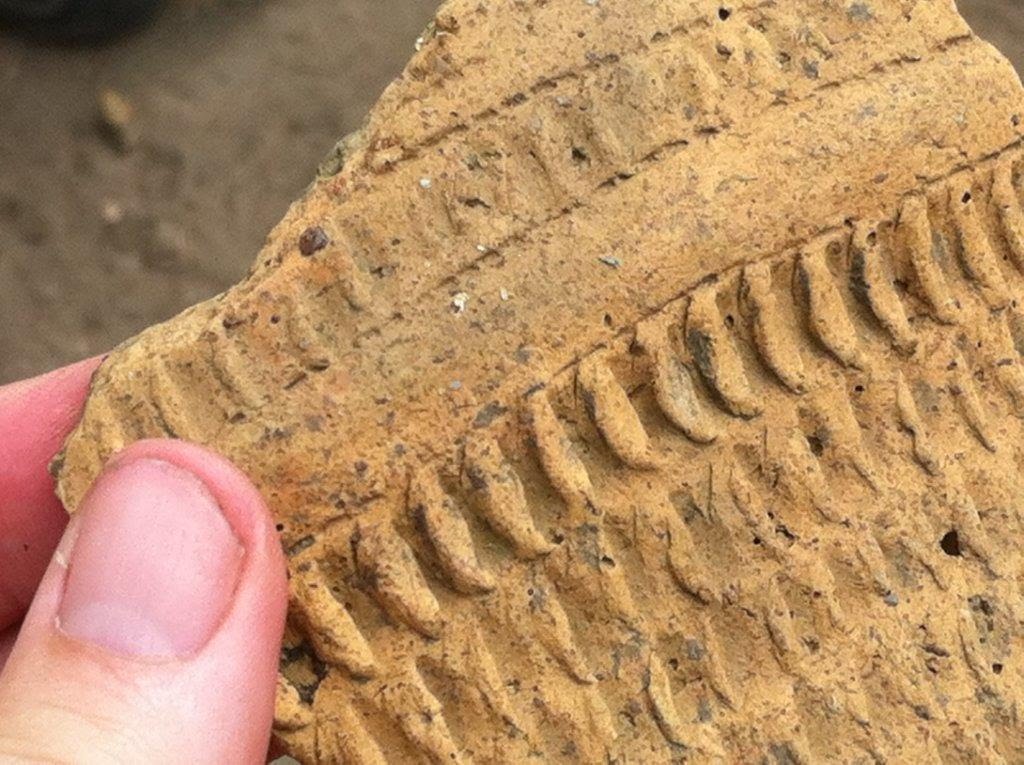
Cromer Road School dig 2015. By Melvyn Dresner.
New member Melvyn Dresner and student archaeologist at Birkbeck College reflects on his first dig with HADAS.
This June, I worked alongside primary school children enjoying their first ventures into archaeology. My interests are in the prehistoric and medieval periods but here we are digging out a 1930’s building that was still standing in the 1960s which still holds a fascination. Archaeology, even if from the recent past, can reveal stuff about life that written sources cannot. Also, as I found from digging in the midst of a community with a school, people can easily see you digging. They show you that they are interested and have all sorts of information to share and questions to ask.
 On the first day we arrived on the green opposite the school. We knew something about the site by looking at parch marks in the grass and followed this by a geophysical survey, which showed a strong result in places. We peeled off the turfs for two trenches. The ground was exceptionally hard and only a few centimetres below the surface we were onto the archaeology – a line of bricks frog up in Trench 2. Trench 1 was opened to help the children learn the techniques and reasons we undertake archaeology and get hands-on experience revealing the past beneath their feet. Trench 2 was where we thought we would need more digging, which was eventually visited by all ages at the school.
On the first day we arrived on the green opposite the school. We knew something about the site by looking at parch marks in the grass and followed this by a geophysical survey, which showed a strong result in places. We peeled off the turfs for two trenches. The ground was exceptionally hard and only a few centimetres below the surface we were onto the archaeology – a line of bricks frog up in Trench 2. Trench 1 was opened to help the children learn the techniques and reasons we undertake archaeology and get hands-on experience revealing the past beneath their feet. Trench 2 was where we thought we would need more digging, which was eventually visited by all ages at the school.
Figure1:Trench 2
 Day two, revealed more concrete in Trench 2, where I was working. We can see that the line of bricks is part of a structure though it’s apparent the structure of the wall is not massively thick. In the rubble there could be another wall.
Day two, revealed more concrete in Trench 2, where I was working. We can see that the line of bricks is part of a structure though it’s apparent the structure of the wall is not massively thick. In the rubble there could be another wall.
Figure2: Excavating trench 2.
Day three is the most revealing day, but we were left scratching our heads. Below the rubble layer we discover concrete steps leading to a concrete floor although the bottom step is cut by a metal pipe. Why have a pipe at the bottom of a step? Answers on a postcard please. As well as brick rubble we found some sort of furniture with springs, a dark blue lamp shade and right at the bottom some tin boxes of uniformed size and shape. These boxes may prove key to explaining the use of the building.
Day four: much speculation on the use of the building. Research in the background suggested that the site could be a gas decontamination centre built during the Second World War before being converted to blood supply. Proximity to the Maw’s pharmaceutical factory was considered relevant. The layout of the building and detail revealed by trenches suggested a certain building typology designed to allow the process of people through gas decontamination. There are standing examples of these buildings elsewhere which seem to support this idea. The tin boxes found on the concrete floor could be a type used for blood transfer kits. These boxes will need closer examination.
Also on day four, three men who were at the school during the late 1940s and early 1950s, remembered the building from when they were pupils. They remembered the building smelled horrible, which may have been chemicals associated with processing, or just unpleasant associations with blood.
Day five was the final day. Speaking to a local brick layer, he had some ideas about how the brick wall was laid and why different techniques were used. We can see how the foundation was laid, the use of mortar to waterproof the wall, and we speculated why the frogs were up or down and about the different bricks used on wall facing inside or outside the building. This needs more thought. What is interesting is that whilst paperwork may only contains fleeting references, the archaeology tells us about different types of activity that allowed people to turn bureaucratic decisions into buildings, and provide blood supplies after (and also most likely) during the war. Careful processing of finds and cross referencing with documentary evidence may reveal stories that can only be told in full though archaeology.
 The Forge Mill Needle Museum, Redditch. By Jim Nelhams.
The Forge Mill Needle Museum, Redditch. By Jim Nelhams.
Travelling in Redditch to a meal with family members, we passed a sign to “Forge Mill Museum”. Having finished lunch, and with time to spare before returning to our hotel, we decided to investigate.
Following the signs led us to a short road, Needle Mill Lane, with a small car park at the end. Here we found a visitor centre and signs to the museum. Unfortunately, the museum was just closing, but we were expecting to visit the area again within a month, so we duly returned.
The visitors centre covered not just the museum, but also the ruins of Bordesley Abbey, of which more in another article. Both the Abbey and Mill are scheduled ancient monuments.
To clear the confusion over the name, it is the Forge Mill Needle Museum. Redditch was at one time the centre of the production of needles in the whole world. In 1866, it is recorded as producing 100 million “needles” per week, many produced in the building which houses the museum. During the 1960s and 1970s, the sole UK producer was Needle Industries in nearby Studley. The company still exists but is now Indian owned and produces most of its products in India under the name Pony Needles.
There are two buildings, one three storey, and the other two, separated by a mill race with an overshot water wheel, fed from a mill pond, which provided power to both buildings. The stream feeding the mill pond was once known as the red ditch, from which the town gets its name. A steam engine, now removed, provided power in times of drought. The current buildings date from about 1828 when there was a major rebuild. The water wheel is run during the day so that some of the machinery can be seen in motion.
Our tour started on the top floor of the east building where there is an amazing display of the types of needles that were produced in the area. These include whaling harpoons, gramophone needles, sewing and knitting needles, dart points, surgical and hypodermic needles, needles for knitting machines and fishing hooks. There is also a short video about the processes used.
The middle floor is available as an exhibition space while the ground floor takes you through the stages of needle production. Needles were cut to the right length from rolls of wire, heated and drawn to the required diameter, shaped, with eyes added if required, sharpened on grind wheels, and hardened before being passed to the second building for polishing. It is this polishing process which required the mill power.
The needles were neatly stacked in bundles of canvas and hessian, soap, grease and emery powder was added, and the bundles securely tied. The bundles, or setts, were the placed in the scouring beds, where they acted as rollers. The mill had 32 of these machines using the mill’s power. They were then rolled for 2 hours at a time, to produce the final polished product. Certain types of needle might need a further 2 hours. Some of these machines, with dummy setts, are still in operation. These were commercially used until 1958.
From 1911 to 1963, the building was known as the Salmon Fly Works, producing fishing tackle.
As with many museums, the building is staffed by volunteers, on this occasion, one gentleman and his cat.
Access to and within the building needs care, with many steps and no lifts. Nevertheless, this museum is well worth a visit – we spent over two hours looking around. (Postcode for satnav – B97 6RR).
Excavating the Prehistoric past of Must Farm. By Sandra Claggett.
In July this year undergraduate students from Birkbeck College were lucky enough to take part on a week’s excavation at this site near Peterborough. The area of Must Farm and its environs are well known for their deep Fen history stretching back to the prehistoric era. As the area became waterlogged due to the rising sea levels after the last ice age, structures built and artefacts left in the soil became well preserved. To cope with the continuing rising sea levels in the Fenland during the Bronze and Iron Age wooden walkways and platforms were constructed and travel by boat began to dominate.
Within the last few years at Must Farm eight Bronze Age log boats which had been carved out of tree trunks have been found in a stretch of preserved prehistoric river channel. A collapsed platform was also found which had been destroyed by fire and preserved as it fell into the river channel, Finds from this included pottery bowls that still had spoon and contents inside, as well as material that had glass beads attached. Also found in this environment and at nearby Flag Fen were swords that have been left as offerings.
 Grid patterns were laid out in the soil during our week long excavation, which were evenly divided into squares and each student would then choose a square to work on (Figure 1).
Grid patterns were laid out in the soil during our week long excavation, which were evenly divided into squares and each student would then choose a square to work on (Figure 1).
Figure 1. (Author’s own photograph)
It was exciting to see that in a lot of places including my own square the Neolithic history was seen just lying on the surface waiting to be found. I recovered worked Flint tools, one piece in particular which some individual all that time ago had spent energy and shown skill to make a sharp serrated edge on both sides. This piece looked like the shape of the fish. I liked to feel that it held a special place for the person that made it. (Figure 2).
 Figure 2. (Author’s own photograph)
Figure 2. (Author’s own photograph)
I also found animal teeth probably from a butchered animal, and burnt stone probably from a fire which indicates cooking nearby. Within my test pit block a feature was found during excavation which contained charcoal burnt stone and some pottery sherds. Due to the fact that the surrounding soil was not burnt it was interpreted that the fire itself was not here but that it had been dug to take the contents of a fire that was elsewhere, so they were cleaning up after themselves! (Figure 3).
Figure 3. (Author’s own photograph)
On a higher surface level some of us were looking for wood chips where we got to feel our way through nice squidgy soil looking for wood that showed it had been worked and had cut marks. (Figure 4).
 Figure 4 (Author’s own photograph)
Figure 4 (Author’s own photograph)
The stratigraphy for this level would be Bronze Age and any worked wood could date to the period of the platform and walkways being built. We were also looking for animal or human footprints that could have been left in the mud as had occurred near the collapsed platform.
During the week I also pieced together fragments of pottery from different pots to see whether we had enough sherds to be able to reconstruct any of them. Looking at the designs on the pottery made me realise the skill in the detail and the beauty in the design of some of these. In some designs you could actually see the thumb imprints from the person that made them. (Figure 5).
 Figure 5 (Author’s own photograph)
Figure 5 (Author’s own photograph)
It makes me wonder what we will leave behind for people in the future to make of us.
The Hanson Logboat. By Jo Nelhams.
During the Kent trip in 2014, HADAS visited the Dover Museum to investigate the Bronze Age Life Gallery and the internationally important Bronze Age boat (see Newsletter September 2014). Later in the year Jim and I visited a friend near Derby and then took the opportunity to visit the Derby Museum. There we found another Bronze Age boat.
 At Hanson’s gravel quarry at Shardlow on the River Trent in 1998, workman spotted what seemed to be a hollowed out tree trunk with stone inside. Doctor Chris Salisbury, an archaeologist, identified it as an ancient Logboat. Excavation took place in 1998-9 and this Logboat was the first to be discovered with what appeared to be its cargo. The cargo was identified as Bromsgrove sandstone, which is found further upstream.
At Hanson’s gravel quarry at Shardlow on the River Trent in 1998, workman spotted what seemed to be a hollowed out tree trunk with stone inside. Doctor Chris Salisbury, an archaeologist, identified it as an ancient Logboat. Excavation took place in 1998-9 and this Logboat was the first to be discovered with what appeared to be its cargo. The cargo was identified as Bromsgrove sandstone, which is found further upstream.
Carbon 14 dating revealed that the Hanson Logboat was about 3,400 years old. Several tools and weapons were found in the quarry, and are also displayed in the museum.
 Shardlow is south east of Derby, but evidence of Bronze Age settlements in the Derby area include Arbor Low stone circle, to the north of Derby, which was visited by members on the trip to Buxton in 2013.
Shardlow is south east of Derby, but evidence of Bronze Age settlements in the Derby area include Arbor Low stone circle, to the north of Derby, which was visited by members on the trip to Buxton in 2013.
Frith Manor House and Frith Grange, Frith Lane, NW7. By Clinton Hudgell.
I was wondering if these two venues would be worth exploring? They were once quite substantial properties.
Frith Manor House is now a stable complex, and Frith Grange is basically part of a Scout Camping Ground.
The original Frith Grange building stood in the “spinney” on the other side (east) of Frith Lane. The Spinney land is also leased by the Scouts of Barnet even though it (The Spinney) forms the boundary screen for the Finchley Golf Club. I can remember seeing the original foundations of the Grange, but it was gradually filled in, used as a dump for all the remains of burnt rubbish from the Camping Ground opposite. The large empty hole in the foundations was commonly known as the “bomb hole” and I suspect that the Grange may have been bombed during the Second World War. (This is not substantiated)
It would be interesting to initially look at the early OS maps of Frith Lane. Does anyone have copies of these maps and perhaps an early painting or photograph of the aforementioned buildings? It would also be interesting to hear of any earlier recollection of these substantial properties.
Please contact the editor of this newsletter (Stephen Brunning) if you can help.
Greetings to new members – Stephen Brunning.
I would like to extend a very warm welcome to all the new members who have joined HADAS since October 2012. They are: Stephen Callway, Sandra Claggett, Jennie Cobban, Melvyn Dresner,
Sevinc Duvarci, Joanna Fryer, Janet Mortimer, Lucy Murray-Davey, Brendan, Caroline & Christine Power, Catriona Prothero, Alec Radosavljevic, David Richman, Stepan Stepanenko, Helene Woodnick and Michele Zoghbi. We look forward to seeing you at a forthcoming event.
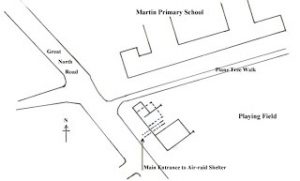
Avenue House at War Exhibition.
This basement exhibition will run until 30th September and tells the story of how Avenue House gave service to the nation on the home front in two world wars – as a RAF hospital & ARP headquarters.
Opening times are: Tues, Weds, Thurs 14:00 – 16:30. Sat, Sun 12:00 – 16:30.
Entry at other times by appointment for school visits, group bookings, as part of a guided tour or in connection with a private booking with an event in the house. Due to the authentic nature and location of this exhibition it is not possible to make it fully accessible to those with restricted mobility. Admission is free but donations are very welcome.
Gladiator Games with the Museum of London – 8th to 16th August.
The publicity for this event is as follows: “In this game of titans, life and death is in your hands. See battle commence on the site of London’s only Roman amphitheatre, hear the crowd roar and steel clash as you choose which warriors walk free. In this live action summer spectacular, we take you back to Roman Londinium with an epic re-enactment of London’s gladiatorial games. Performers take to the stage for battle, an Emperor presides and the crowd picks its side. Westeros has nothing on Londinium”
Show times: Evenings: 10 & 14 Aug, 7-8.00 pm Weekends: 8, 9, 15 & 16 Aug, 12-1.00 pm & 3-4.00pm. Step into Londinium with pre-show entertainment in the Guildhall Yard from an hour before each show. A bar serving drinks and snacks will be open before and during the show.
Ticket prices: Adult: £15; Child: £10; Concession: £12.50
Location: The Gladiator Games are held in the Guildhall Yard, off Gresham Street, London EC2V 5AE.
Nearest tube: St Paul’s, Bank, Moorgate (5 minute walk).
Nearest DLR: Bank (5 minute walk)
Nearest overground: Moorgate (5 minute walk)
For any enquires relating to specific access requirements please contact box office on 020 7001 9844. This event will not be cancelled due to bad weather; we advise that you dress appropriately as the amphitheatre seating is open air.
Other Societies’ events, compiled by Eric Morgan.
Tuesday 8th September, 7.45pm. Amateur Geological Society. The Parlour, St Margaret’s Church, Victoria Avenue N3 1BD (off Hendon Lane). Mineralogy at the Natural History Museum: more than the earth’s treasury. Talk by Prof Andy Fleet (Natural History Museum).
Wednesday 9th September, 9am. Mill Hill Historical Society. Coach trip to East Grinstead & Nymans. Depart Hartley Hall, Flower Lane NW7 at 9am. Latest date for booking is Thursday 20th August to Keith Dyall, 26 Millway, NW7 2RB. Price is £26.50 (National Trust members £17.50). Telephone 020 8959 7147 or 07788 677103. Please send SAE together with cheque payable to “Mill Hill Historical Society” stating your name, address, telephone number and email address. Will leave for home at 5pm.
Thursday 10th September, 7.30pm. Camden History Society. Camden Local Studies Archive Centre, 2nd floor, Holborn Library, 32-38 Theobalds Road, WC1X 8PA. How Ian Nairn came to love London. Talk by Gillian Darley. Visitors £2.
Friday 11th September, 7.45pm. Enfield Archaeological Society. Jubilee Hall, 2 Parsonage Street (junction of Chase Side), Enfield EN2 0AJ. Prehistoric Archaeology. Talk by Jon Cotton (Vice-President). Visitors £1. Refreshments, sales and information table from 7.30pm.
Monday 14th September, 3pm. Barnet Museum & Local History Society. Church House, Wood Street, Barnet (opposite museum). The development of Wrotham Park Mansion. Talk by Charles Dace. Visitors £2. Also Saturday 19th September. Coach outing to Bodiam Castle and Rye. For details please contact Pat Alison at 37 Ladbroke Drive, Potter Bar, Herts EN6 1QR. Telephone 01707 858430 or Barnet Museum on 020 8440 8066.
Wednesday 16th September, 6.30pm. Willesden Local History Society. Willesden Green Library, High Road, (corner of Brondesbury Park NW10. Visit to the new Brent Archives. With Emma Treherne. NOTE earlier start time. Also Saturday 12th September. Willesden Green Library re-opens. Willesden Local History Society will have a stand here.
Wednesday 16th September, 7.30pm. Islington Archaeology & History Society. Islington Town Hall, Upper Street N1 2UD. Recreating a 19th century house in Canonbury Square. Talk by Gary Butler (architect). Visitors £1.
Saturday 19th & Sunday 20th September. London Open House Weekend. FREE access to over 800 buildings. Details at www.openhouselondon.org.uk. INCLUDING: Saturday 19th 10am-4pm. Myddleton House Gardens, Bulls Cross Enfield EN2 9HG. Magnificent house of E.A. Bowles (HADAS did resistivity here). Saturday 19th & Sunday 20th 11am-4pm. Three Mills House Mill, Three Mills Lane, Bromley-by-Bow, E3 3DU. 20 minute guided tour of the grinding stones and water wheels is available at this historic site. (HADAS had a talk on the mill last year). Saturday 19th & Sunday 20th, 1-5pm. Friends of Brompton Cemetery. South Lodge, Brompton Cemetery, Fulham Road SW10 9UG. The chapel will be open with guided tours starting at 2pm on both days. Refreshments available.
Wednesday 23rd September, 7.45pm. Friern Barnet & District Local History Society. North Middlesex Golf Club, The Manor House, Friern Barnet Lane N20 0NL. Baxendale: Past, Present & Future. Talk by Brian Hosier. Visitors £2. Refreshments.
Friday 18th September, 7.45pm. Wembley History Society. English Martyrs’ Hall, Chalkhill Road, Wembley HA9 9EW (top of Blackbird Hill adjacent to church). Kingsbury from the air in the 1920’s & 30’s. With Jim Moher. £2.
Wednesday 16th September, 6pm. Gresham College at Museum of London. 150 London Wall, EC2Y 5HN. 1665: London’s Last Great Plague. Talk by Prof. Vanessa Harding. FREE.
Many thanks to this month’s contributors: Sandra Claggett, Don Cooper, Melvyn Dresner,
Clinton Hudgell, Eric Morgan, Jim Nelhams, Jo Nelhams, Peter Pickering and Stewart Wild.



 Further reports will appear in future newsletters.
Further reports will appear in future newsletters.
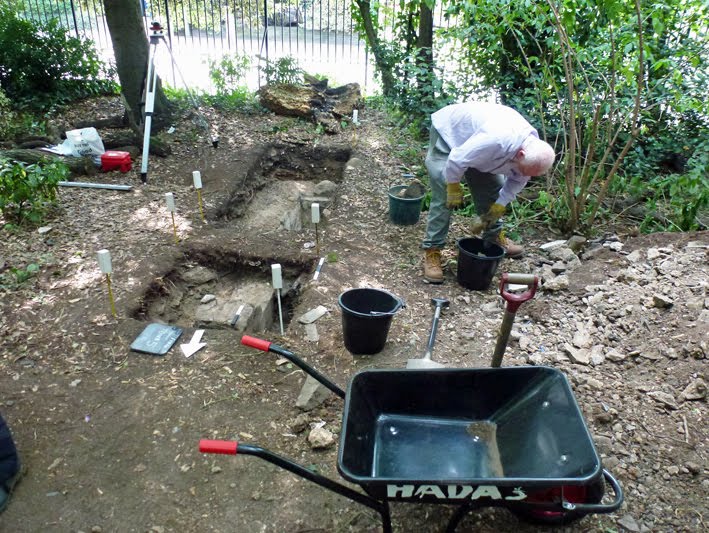




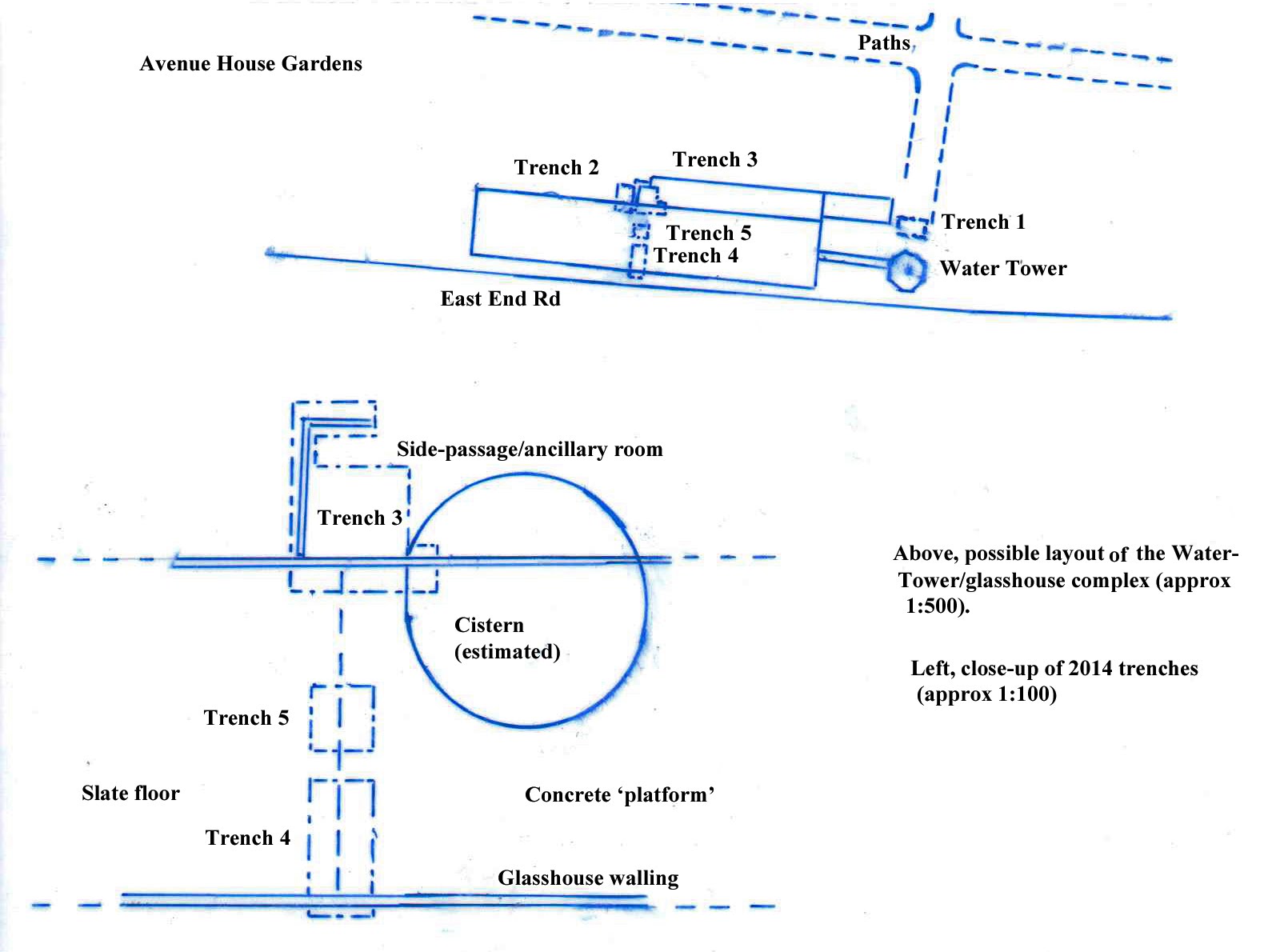


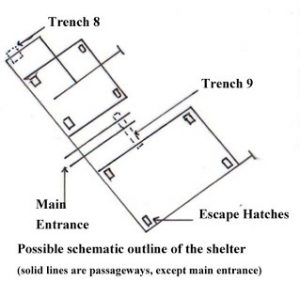
 A Trench story Roger Chapman
A Trench story Roger Chapman